Welcome
 If you're looking for a few sets of assignments with these types of problems, please follow the links below.
If you're looking for a few sets of assignments with these types of problems, please follow the links below.
Homework Sets #1 - 3: Click Here
Additional Problems: Click Here
If you'd like a PowerPoint on this topic, please go down to tab 4.6 below.
Be sure to like my FaceBook page to get updates when materials like this are posted.
Geometry (2D)
Unit 4
Vocabulary: Know precise definitions of acute, obtuse, right angle, reflex, equilateral, isosceles, congruent, similar, regular, pentagon, hexagon, octagon, rectangle, square, kite, rhombus, parallelogram, trapezoid, and simple solid figures.
Definitions: Know precise definitions of angle, circle, perpendicular line, parallel line, and line segment, based on the undefined notions of point, line, distance along a line, and distance around a circular arc.
To download a printable copy of the Teacher's Reference, please click here.



Here are some screen shots from the PowerPoint.


To download a printable copy of the practice problems, please click here.

To download a copy of the textbook materials, which are a fantastic student reference, please click here.



Line and rotational symmetry in 2D and 3D. e.g., know properties of triangles, quadrilaterals, and circles directly related to their symmetries. For example, given a rectangle, parallelogram, trapezoid, or regular polygon, describe the rotations and reflections that carry it onto itself. Recognize symmetry properties of the prism and the pyramid.

|
| Click on the PDF icon to download a Lesson Guide that will pace the PowerPoint. Click on the PowerPoint icon to download the PowerPoint Lesson.
The lessons are intentionally over-built with more material than the time will allow. This way you have more options on how to best serve the needs of your students.
|
For a printable version of this homework, please click here.



Angles formed by parallel lines and transversals, and their relationships.

To download a printable copy of the assignment, please click here.



Hierarchy of quadrilaterals.
|
| Click on the PDF icon to download a Lesson Guide that will pace the PowerPoint. Click on the PowerPoint icon to download the PowerPoint Lesson.
The lessons are intentionally over-built with more material than the time will allow. This way you have more options on how to best serve the needs of your students.
|


If you'd like a printable version of the homework, you can download it by clicking here.



Properties of Polygons

|
| Click on the PDF icon to download a Lesson Guide that will pace the PowerPoint. Click on the PowerPoint icon to download the PowerPoint Lesson.
The lessons are intentionally over-built with more material than the time will allow. This way you have more options on how to best serve the needs of your students.
|



Construction. Make formal geometric constructions with compass and straight edge only. Copy a segment; copy an angle; bisect a segment; bisect an angle; construct perpendicular lines, including the perpendicular bisector of a line
segment. Construct an equilateral triangle, a square, and a regular hexagon inscribed in a circle. Construct the inscribed and circumscribed circles of a triangle. Construct a tangent line from a point outside a given circle to the circle.
Angle measurement in degrees. Read and make scale drawings.
Basic Geometric Constructions
Note: This PowerPoint is designed to allow students to have concise but thorough notes to copy on how to perform the constructions listed below. These constructions are easy to learn, but also easy to forget. Students can have difficulty figuring out how the construction is from just looking at a completed construction.
The animations are sufficient to give students an idea. However, it is best if you can demonstrate on a document camera, show a video, or even better, walk around the room and help students as needed (and have students help each other).
The constructions covered in this lesson are:
- Copy and angle
- Copy a line segment
- Bisect an angle
- Perpendicular bisector
- Triangle
Big Idea
When constructing basic shapes students get a more concrete understanding of the properties of these shapes. Students need to understand how to accurately use geometric construction tools.
Key Knowledge
This lesson is written for Cambridge IGCSE, however, the constructions apply to all geometry. Students need to understand how to do the basic constructions listed.
Pro – Tip
Accuracy is king. Ensure that you’re the lines are aligned between the protractor and whatever is being measured or drawn. Have a light touch with a compass as it will move if you press too hard.
Here are some screen shots from the lesson.





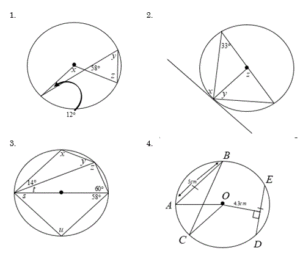
Circles and angles created with circles and lines.


Similarity. Calculation of lengths of similar figures. Area and volume scale factors. Use scale factors and/or angles to check for similarity. Use of the relationships between areas of similar figures and extension to volumes and surface areas of similar solids.

Screen shots from the lesson.



To download a printable copy of the homework, please click here.
















